A Journey of Resilience, Ingenuity, and Seamless Integration: The Transformative Power of the Udhampur-Srinagar-Baramulla Rail Link
India’s vast and diverse landscape has long been a mosaic of cultures, traditions, and regional identities. Yet, amidst this tapestry of diversity, a unifying force has emerged – the mighty railways. Like a thread woven through the fabric of the nation, the railways have connected the farthest reaches of the country, bringing people, goods, and ideas together in a symphony of progress and unity.
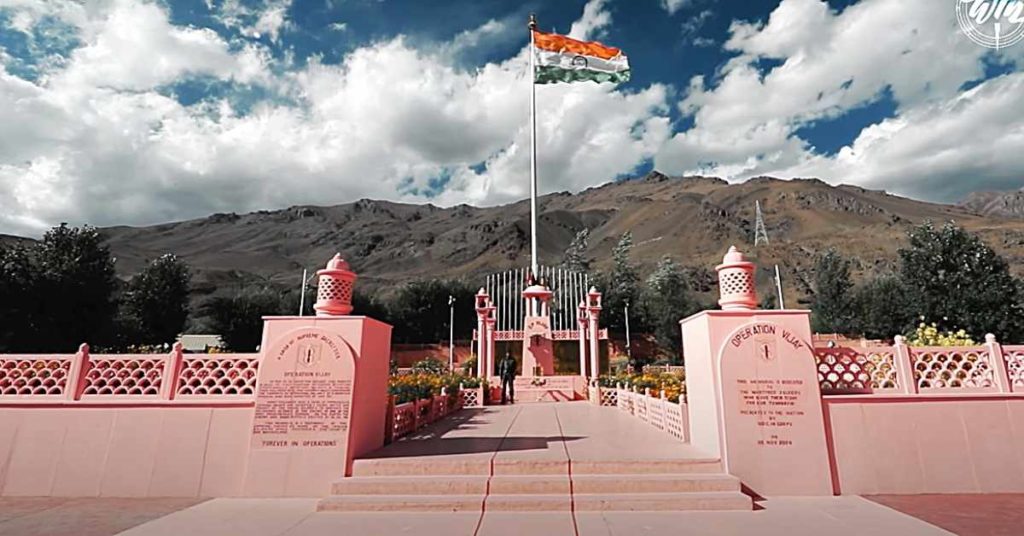
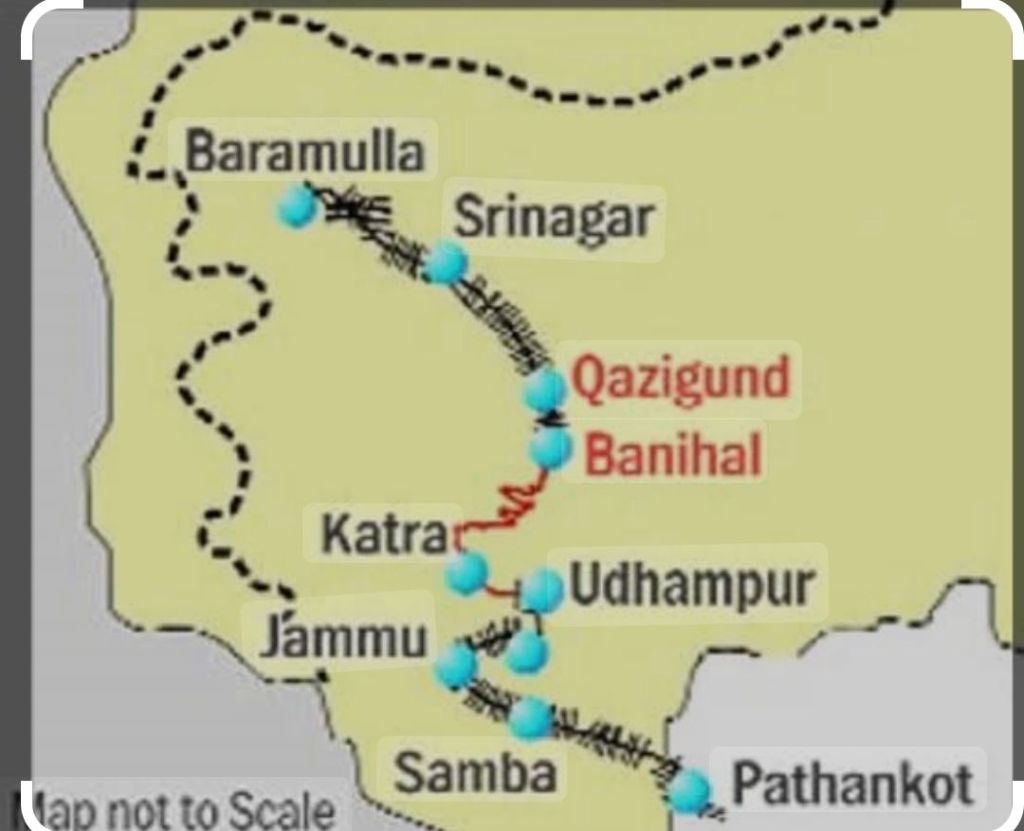
Nowhere is this more evident than in the picturesque region of Kashmir, long considered the crown jewel of the Indian subcontinent. For decades, the challenges of terrain and geography had kept this enchanting land isolated, accessible only through arduous road journeys. But now, a remarkable feat of engineering has changed the game, as the Udhampur-Srinagar- Baramulla Rail Link (USBRL) project nears completion, poised to usher in a new era of connectivity and integration.
The Journey Begins with Connecting the Unconnected. The Udhampur-Srinagar- Baramulla Rail Link project, a dream long cherished by the people of Jammu and Kashmir, is a true testament to the transformative power of India’s Railways. Conceived in the 1990s, the USBRL project aimed to bridge the gap between the Kashmir Valley and the rest of the country, providing a reliable and all-weather mode of transportation that would unlock the region’s vast potential.

The sheer scale and complexity of the endeavor were staggering. Spanning a distance of over 272 kilometers, the railway line would have to navigate through some of the most challenging terrain in the world, traversing mountains, valleys, and the formidable Pir Panjal range. The project would require the construction of an intricate network of bridges, tunnels, and viaducts, pushing the boundaries of engineering and technology.
But the Indian Railways, with its unwavering commitment to connectivity and development, was undaunted by the task at hand. Undeterred by the daunting obstacles, teams of engineers, technicians, and construction workers toiled tirelessly, driven by a vision of seamless integration and the promise of a brighter future for the people of Jammu and Kashmir.

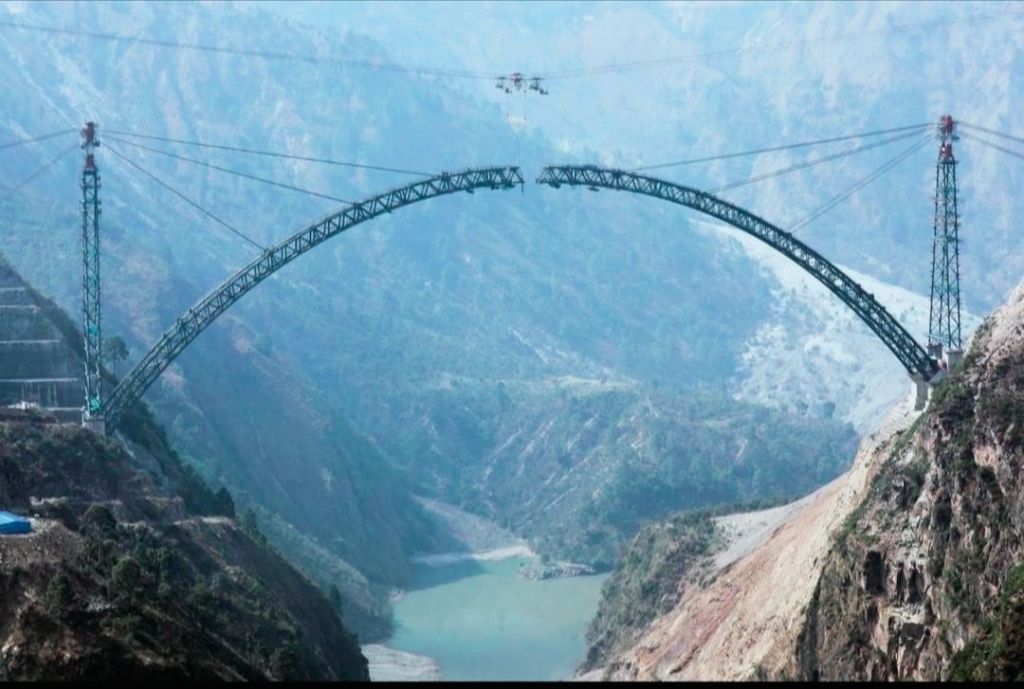
The rail link conquered the Peaks, Bridging the Divide. As the USBRL project progressed, each milestone achieved represented a triumph over the formidable natural barriers that had long kept Kashmir isolated. The construction of the iconic Chenab Bridge, a feat of engineering that defied the laws of gravity, stood as a testament to the sheer determination and ingenuity of the Indian Railways.
Spanning the mighty Chenab River, this marvel of modern architecture rises 359 meters above the valley floor, making it the world’s highest railway bridge. The bridge’s elegant design, with its unique “bird’s nest” configuration, not only serves as a vital link in the railway network but also stands as a symbol of the nation’s unwavering spirit and commitment to conquering the most challenging of landscapes.

But the USBRL project was not just about building bridges and tunnels; it was about forging connections, both physical and emotional, between the people of Kashmir and the rest of India. As the railway line steadily advanced, it became a conduit for the exchange of ideas, cultures, and economic opportunities, breaking down the barriers that had long kept the region isolated.
The introduction of the Banihal-Khari- Sumber-Sangaldan section, an integral part of the Katra-Banihal route, marked a significant milestone in this journey of integration. This operational stretch, completed at an estimated cost of Rs. 15,836 crores, features a remarkable array of engineering marvels, including the longest tunnel in the country – Tunnel-50, spanning an impressive 12.77 kilometers.

Alongside these towering feats of engineering, the project also showcased a deep commitment to safety and sustainability. Eleven additional tunnels, totaling 43.37 kilometers, and three escape tunnels spanning 30.1 kilometers, were meticulously constructed to ensure the well-being of passengers and the overall integrity of the railway network.
As the USBRL project inched closer to completion, its impact began to reverberate throughout the region, touching the lives of countless individuals and communities. The introduction of this transformative railway network has ushered in a new era of economic and social development, unlocking the vast potential of Jammu and Kashmir.

One of the most tangible benefits has been the boost to tourism, a vital pillar of the local economy. With the railway line providing reliable and convenient access to the region, the flow of visitors has surged, breathing new life into the tourism industry and creating myriad employment opportunities for the local populace. From renowned destinations like Gulmarg and Pahalgam to the stunning natural landscapes that dot the Kashmir Valley, the USBRL project has made these wonders more accessible than ever before.

But the impact of the railways extends far beyond the tourism sector. The improved connectivity has also revolutionized the supply chain, ensuring the seamless transportation of essential goods and commodities to the region. This has not only stabilized prices and boosted food security but has also fostered the growth of local industries and small businesses, creating new avenues for economic prosperity.
Furthermore, the USBRL project has become a catalyst for social integration, breaking down the geographical and psychological barriers that had long divided the people of Kashmir from the rest of India. As the railway line brings individuals and communities closer together, it has facilitated the exchange of ideas, cultures, and experiences, fostering a deeper sense of unity and shared identity.

The Railway’s Marble is A Symbol of Unity. As the Udhampur-Srinagar-Baramulla Rail Link project nears its final stages, it has become more than just a transportation network – it has transformed into a symbol of unity, a marble that seamlessly connects the diverse tapestry of India.
Much like the intricate veins running through the finest marble, the railways have become the lifeblood that courses through the nation, weaving the diverse regions and cultures into a cohesive whole. Just as the unique patterns and hues of marble are a testament to the Earth’s natural wonders, the USBRL project has become a reflection of India’s own rich diversity, a living embodiment of the country’s ability to overcome daunting challenges and emerge stronger, more united, and more prosperous.

The project’s completion will not only revolutionize the way people and goods move through the region but will also serve as a powerful reminder of the transformative power of connectivity. By linking the far-flung corners of Jammu and Kashmir to the rest of the country, the railways have become a conduit for the exchange of ideas, cultures, and economic opportunities, fostering a sense of shared identity and mutual understanding.The Udhampur-Srinagar-Baramulla Rail Link project is more than just an engineering marvel; it is a testament to the resilience, ingenuity, and unwavering commitment of the Indian Railways. Like a marble that seamlessly integrates the diverse elements of the nation, this railway network has become a symbol of unity, a physical manifestation of the country’s unbreakable spirit.
As the project nears its completion, the people of Jammu and Kashmir, and indeed the entire nation, stand on the cusp of a new era of connectivity and prosperity. The railways have not only transformed the landscape of the region but have also touched the lives of countless individuals, unlocking new economic and social opportunities.

The USBRL project is a shining example of how infrastructure development can serve as a catalyst for holistic growth, fostering unity, empowering communities, and paving the way for a future of boundless possibilities. As the trains begin to traverse the mountains and valleys of Kashmir, they will carry with them the hopes and dreams of a nation united, a testament to the power of connectivity and the unwavering spirit that defines the very essence of India.
Visit arjasrikanth.in for more insights