Revolutionizing India’s Energy Landscape: The Dual Path of Pumped Storage Plants and Repurposed Coal Mine
India’s energy sector is undergoing a monumental transformation, driven by two ground breaking initiatives: the proliferation of Pumped Storage Plants (PSPs) and the repurposing of old coal mines into green energy sites. Supported by Coal India and its subsidiary, Western Coalfields Limited (WCL), these initiatives represent a significant shift towards sustainable practices in the country’s energy sector. This comprehensive article explores the multifaceted aspects of PSPs, delves into the green revolution in coal mines, and examines the interconnected future prospects of these initiatives.
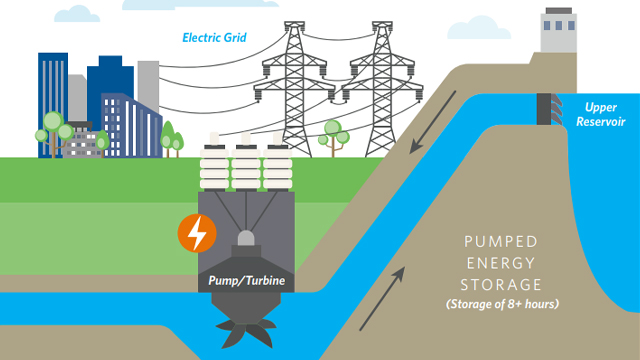
Pumped Storage Hydropower (PSH) stands as a cornerstone in India’s energy landscape, offering essential peaking power, grid stability, and efficient energy storage through dual-reservoir technology. Classified into open-loop and closed-loop systems, PSH caters to the diverse demands of India’s energy needs. The ambitious endeavour by the Greenko Group to establish India’s largest pumped storage project in Madhya Pradesh, with a capacity of 1,440 MW, underscores a commitment to sustainable energy practices, marking a substantial stride toward a greener future. An insightful analysis of costs and potential, now revised at an impressive 106 GW, showcases the economic viability of pumped hydro storage, aligning seamlessly with the government’s ambitious energy targets. Despite environmental and regulatory challenges, proactive policy interventions indicate a favourable environment for pumped storage initiatives, accentuating the government’s unwavering commitment to fostering sustainable energy solutions.

Union Coal Ministry, unveiled the transformative vision of Coal India and WCL to repurpose abandoned mines into green energy sites. With four to five defunct mines identified in the Chhindwara Pench region, the initiative symbolizes a departure from traditional coal-centric practices towards embracing renewable energy solutions. Senior official’s personal inspection of these sites underscores the government’s commitment to exploring new avenues for sustainable energy development. Aligning with the broader push towards sustainability, Coal India’s plan to repurpose old mines for green energy sites mirrors the Its vision. The identification of mines in the Chhindwara Pench region for conversion into solar and pumped storage projects signifies a proactive and innovative approach to land utilization.
The initiative to convert closed mines into green energy sites aligns with the global momentum towards eco-friendly practices. By repurposing land once dominated by coal extraction, India demonstrates its commitment to transitioning towards cleaner and more sustainable energy sources. The integration of solar and pumped storage projects represents a multifaceted approach towards maximizing resource utilization and minimizing environmental impact. The repurposing of closed mines for green energy projects holds immense potential for India’s energy landscape. Beyond addressing environmental concerns associated with abandoned mines, this initiative unlocks new opportunities for renewable energy generation. The vast land available at these sites presents an ideal canvas for the deployment of solar panels and the construction of pumped storage facilities, tapping into India’s abundant solar resources and hydroelectric potential.

The transition from coal-centric operations to green energy sites carries both economic and environmental implications. Not only does it create opportunities for job creation and economic development in regions previously reliant on coal mining, but it also contributes to reducing carbon emissions and mitigating environmental degradation. By repurposing existing infrastructure, India showcases its commitment to sustainable development and responsible resource management. The repurposing of old mines for green energy sites holds far-reaching implications, transcending economic benefits. It addresses environmental concerns associated with abandoned mines, contributes to cleaner energy generation, and signifies a strategic move towards responsible resource management and environmental stewardship.

Coal India’s initiative to repurpose closed mines into green energy sites marks a paradigm shift in India’s energy sector. By embracing renewable energy solutions and incentivizing coal gasification projects, India demonstrates its readiness to transition towards a cleaner and more sustainable energy future. The conversion of abandoned mines into hubs of renewable energy production reflects a forward-thinking approach to resource utilization and environmental stewardship. As India continues to pursue its renewable energy goals, initiatives like these serve as shining examples of innovation and progress in the quest for a greener planet.
As India takes a dual leap towards a sustainable energy future, embracing pumped storage projects and repurposing old coal mines, the nation positions itself at the forefront of global innovation in the energy sector. The synergy between these initiatives marks a strategic and holistic approach to addressing energy needs while minimizing environmental impact. As the country advances towards cleaner and more resilient energy infrastructure, these initiatives stand as beacons of progress and set the stage for a greener and brighter future.
visit arjasrikanth.in for more insights