“Navigating the Waves of Disruptive Technologies: Impact on Employment and Socio-Economic Dynamics”
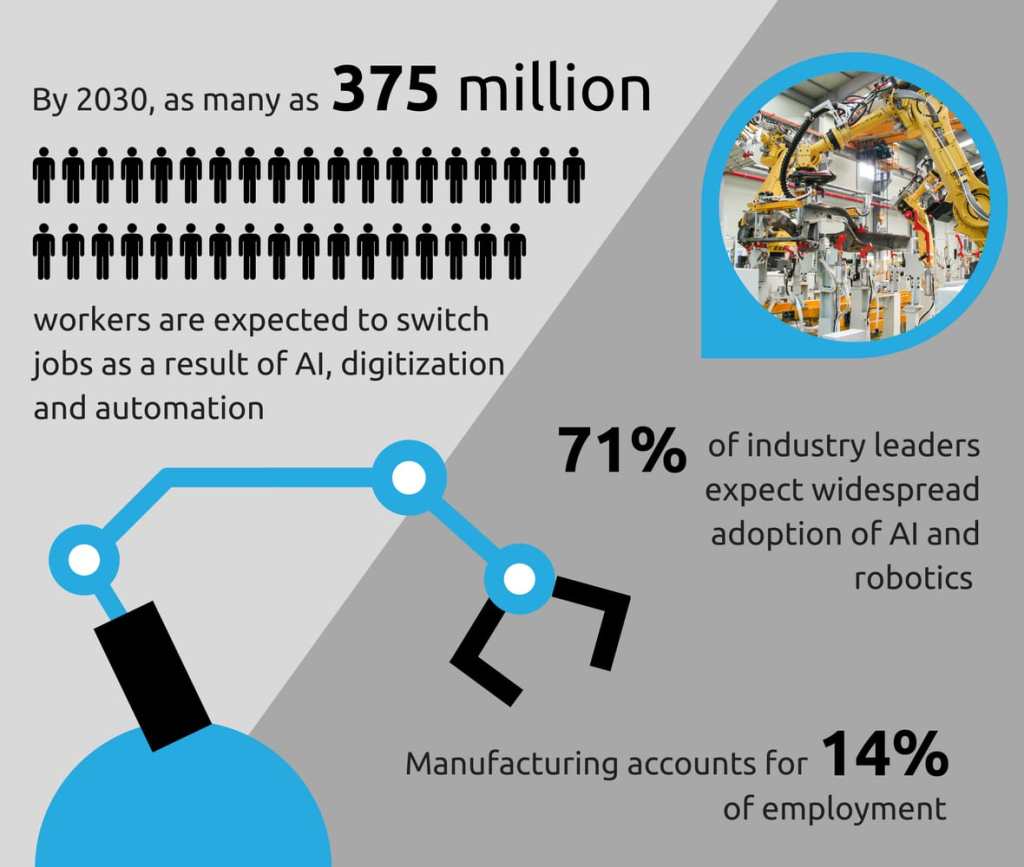
The surge of disruptive technologies is reshaping the landscape of industries, leaving an indelible mark on how consumers interact with products and services. However, beneath the surface lies a complex interplay between innovation and employment, sparking debates on job creation, displacement, and the socio-economic consequences. This article delves into the multifaceted impact of disruptive technologies, exploring the nuances of their influence on job markets and societal well-being.
Disruptive technology, characterized by innovations that revolutionize existing markets and business models, carries the potential to reshape industries fundamentally. From 5G technology to artificial intelligence and advanced virtual reality, these technologies introduce new products, services, and processes, altering traditional paradigms and leaving an enduring impact on how business is conducted.
Disruptive technologies present a paradox in the employment landscape. While they open new vistas in industries such as software development, data analytics, and automation, they simultaneously pose a threat to jobs dependent on manual labor or conventional methodologies. The net effect on employment is a delicate equilibrium, with the potential for positive growth in the long run as innovation and productivity drive the creation of new jobs and industries.
The adoption of disruptive technologies heralds positive effects on the economy, yet the transition is not without costs. The displacement of existing industries, workers, and institutions represents a significant challenge. Balancing the gains with the losses becomes pivotal in understanding how emerging economies can harness the benefits of disruptive technologies while mitigating adverse effects on established sectors.
The employee life cycle undergoes transformation with the integration of technology. Human resources professionals leverage HR technology throughout the entire journey, from recruitment to departure. The use of tools such as HRIS and performance management systems streamlines data management, performance assessment, and training, ushering in a new era of efficiency and effectiveness.
Disruptive innovation, whether in the form of low-end or new-market disruption, poses challenges for incumbent organizations. In its early stages, disruptive innovations may not perform as well as existing products, leading to a tendency for organizations to overlook their potential. High risks accompany disruptive innovation, particularly when catering to a small segment initially.
The disruptive technologies, particularly AI, automation, and digitization, redefine employment generation. However, the narrative often sidesteps the insecurities faced by the unemployed youth. The reduction in employment opportunities, as witnessed in various sectors, raises concerns about the socio-economic impacts, potential increases in crime, and shifts in societal dynamics.

As disruptive technologies continue to shape the future, a nuanced understanding of their impact on employment and society is imperative. The ongoing debate surrounding the advancements in AI, automation, and digitization should not overshadow the critical discussion on unemployment, inflation, and the skills needed for the future workforce. Navigating these waves requires a comprehensive approach, addressing both the benefits and challenges to ensure a balanced and sustainable future for employment and socio-economic well-being. The disruptive technology revolution is not merely about innovation; it is about shaping a future where progress is inclusive and mindful of its societal footprint.
Special thanks to Vinay Kuamr IRS , for contributing insightful thoughts to this article.
Visit arjasrikanth.in for more insights